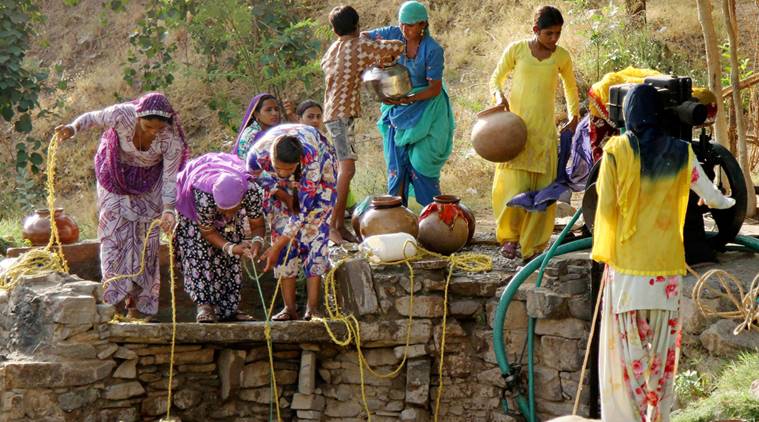
It’s not by chance that the desert state has given an adequate water harvesting technique which is appearing as an inspiration for other countries as well. Rajasthan’s Mukhyamantri Jal Swawlamban Abhiyan created quite a buzz with its unique “staggered trenches” rooftop harvesting technique.
While introducing Mukhyamantri Jal Swawlamban Abhiyan, the state govt. thought of conserving every drop of potable water. Resultantly, Rajasthan’s tribal areas of Banswara district witnessed an auspicious rise in the ground water levels. This brought the required moisture to make the land fertile. The technique opted for this mission has been opted by many states of the country. Not only this, many African countries opted this unique method of water conservation.
CM Vasundhara Raje’s attempt to make Rajasthan villages self-sufficient brought out good colours. Rajasthan’s 60% land is sandy and that’s why state govt. took this brave move. As per the current scenario, the land water is catering to the 90% potable water needs of people, also 60% of this is in use for irrigation purposes. This is causing exploitation of land water and hence the land water levels are dropping rapidly.
CM Raje has long term future vision for Rajasthan which is quite apparent in Mukhyamantri Jal Swawlamban Abhiyan. The scheme is dedicated to raising up the underground water-levels and it has been given the title of “Jan Andolan” (mass movement).
State govt. has assured that the scheme has improved the ground water levels of 3.5 thousand villages and by the year 2019, they are expecting to bring this improvement in 22,000 villages.
The technique of “staggered trenches” was exclusively run in the tribal villages like Tejpur, Lodhakhoda and Khorapada. Under this technique, pits of different lengths are dug in equal distances from each other. This is made this way to ensure that no water is wasted during rains and all get collected in the digs.
A large dig in the form of a pond is made so that the rain water gets overflowed in those ponds. The collected water in pond and digs penetrate in the land and bring moisture to it.
It serves the dual purpose of creating moisture in the land and increasing the underground water levels.